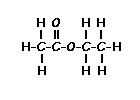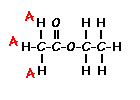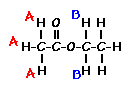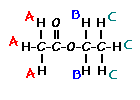| 1H NMR Spectroscopy for CHM 222L Professor: S. Bruce King | Programming & Design: Yue-Ling Wong |
Topics
>>>
Practice >>>
|
Splitting
NMR provides information on how many hydrogen neighbors exist for a particular hydrogen or group of equivalent hydrogens. In general, an NMR resonance will be split into N + 1 peaks where N = number of hydrogens on the adjacent atom or atoms. If there are
no hydrogens on the adjacent atoms, then the resonance will
remain a single peak, a singlet.
Predict the splitting patterns for the labeled hydrogens by drawing the peaks, represented by lines. Drag to draw the lines. Double-click on the line the delete it. (Hint: also note the height ratio of the peak and the distance between peaks.) For ethyl acetate, 1. Draw the
splitting pattern for the hydrogens labeled A.
2. Draw the
splitting pattern for the hydrogens labeled B.
3. Draw the
splitting pattern for the hydrogens labeled C. |